Carbon Footprint
Each human activity consistently affects the environment. One of such activities contributes to the emission of greenhouse gases, directly (such as waste incineration) and indirectly (such as using the electricity produced by thermal power stations). Greenhouse gases emitted have led the heat introduced to the earth trapped in the earth atmosphere and subsequently create a global warming. The amount of greenhouse gases emitted associated with human activities are called carbon footprint. It is important to understand these carbon footprints in order to learn the magnitude of the impact produced by each of our activity.
There are two types of carbon footprints namely primary carbon footprint and secondary carbon footprint. Primary carbon footprint is carbon footprint produced by the direct combustion process of fossil fuel, such as the use of motor vehicles. Whereas, secondary carbon footprint, is carbon footprint produced by the cycle process of products used, ranging from the production process down to the degradation process. An example of this secondary carbon footprint is products consumed daily (normally is in the form of food). Thus the more food we consume, the greater the carbon footprint.
Then how can we learn about the magnitude of the carbon footprints produced by our activities? As a matter of fact, there are numerous methods of carbon footprint calculation in the internet. In general, there are many elements which can be input into the calculation of carbon footprint. For example is the calculation of carbon footprint of individual or domestic activities. Thus, the activities calculated may include food consumption, travel activities, as well as consumptin of domestic electricity.
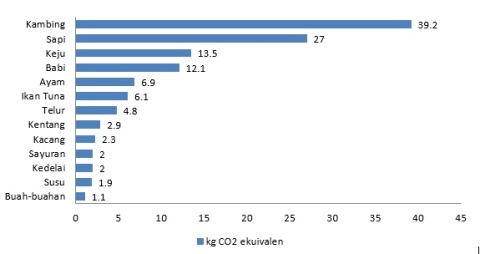
Food consumption includes whether the food consumed leave a great carbon footprint content or not. Types of food containing great carbon footprint normally include meat produts, while vegetables are among the types of food with low carbon footprint. Following is the carbon content of various types of food, as excerpted from the Environmental Working Group (EWG).
Carbon footprint left by travel activities may include the types of vehicle used, whether it is a private vehicle (car or motorcyle) or public transportation (bus, trains, or airplane). Calculation of carbon footprint for private vehicle may include types of fuel used. As excerpted from the United States Energy Information Administration (EIA), the amount of greenhouse gas emission of aviation turbine fuel is 2.20 kg of CO2/liter, biosolar is 2.50 kg of CO2/liter, solar is 2.68 kg of CO2/liter, while gasoline is 2.35 lg of CO2/liter respectively. Therefore, to determine the amount of our carbon footprint produced by our travel activities, may be calculated by the amount of fuel we consume.
Meanwhile for domestic consumption, generally it is calculated by the total kWh of electricity consumed within a year. Carbon footprint of domestic electricity consumption depends on the type of powerplant in use. They may be coal energy plants (such as those used in Indonesia), diesel power plants, nuclear power plant, or renewable energy power plants (such as solar, winds, geothermal, or hydropower). (Jihan A. As-sya’bani)

